Python实现图像全景拼接

Contents
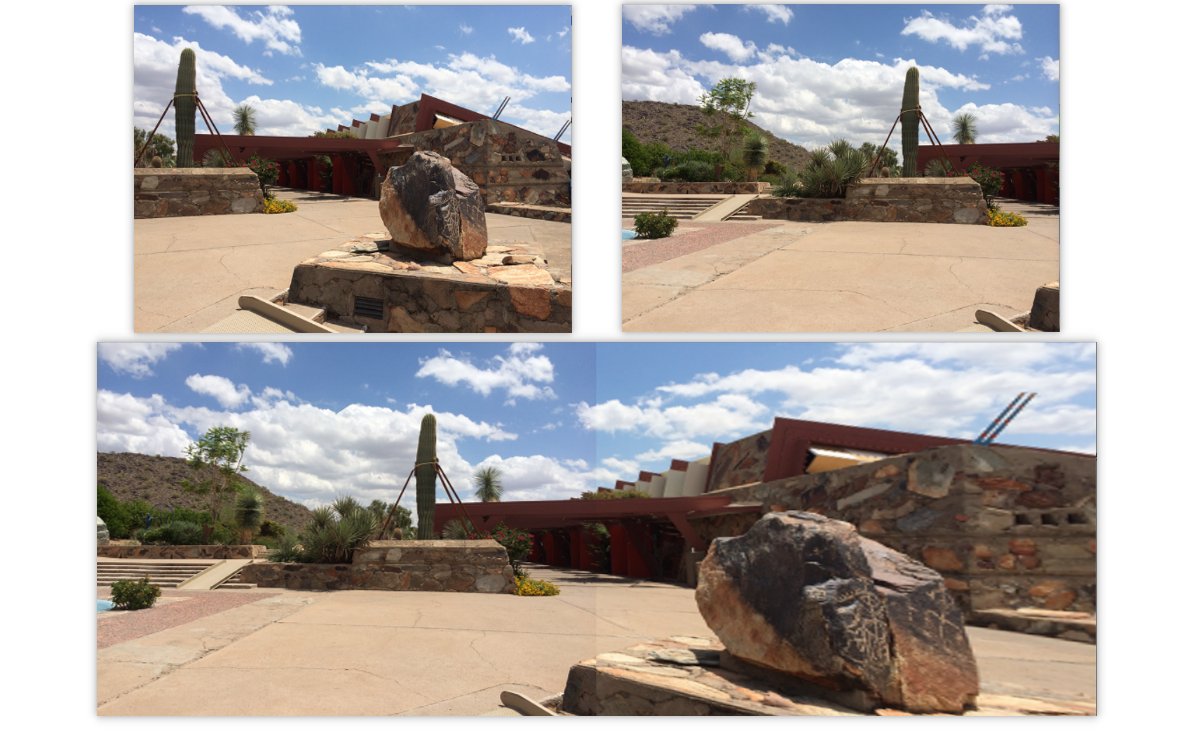
目标:将数张有重叠部分的图像通过特征点检测,匹配,图像变换拼成一幅无缝的全景图或高分辨率图像
在图像拼接中首先利用SIFT算法提取图像特征进而进行特征匹配,继而使用RANSAC算法对特征匹配的结果进行优化,接着利用图像变换结构进行图像映射,最终进行图像融合。
在图像拼接过程中,运用SIFT局部描述算子检测图像中的关键点和特征,SIFT特征是基于物体上的一些局部外观的兴趣点而与影像的大小和旋转无关。对于光线、噪声、些微视角改变的容忍度也相当高,所以用来检测要拼接图像的特征及关键点就很有优势。而接下来即步骤三是找到重叠的图片部分,连接所有图片之后就可以形成一个基本的全景图了。匹配图片最常用的方式是采用RANSAC(RANdom SAmple Consensus, 随机抽样一致),用此排除掉不符合大部分几何变换的匹配。之后利用这些匹配的点来估算单应矩阵”(Homography Estimation),也就是将其中一张图像通过关联性和另一张匹配。
使用的算法:
1. 利用SIFT方法检测特征点
def detectAndDescribe(image):
# 将彩色图片转换成灰度图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 建立SIFT生成器
descriptor = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create()
# 检测SIFT特征点,并计算描述子
(kps, features) = descriptor.detectAndCompute(image, None)
# 将结果转换成NumPy数组
kps = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kps])
# 返回特征点集,及对应的描述特征
return (kps, features)2. 将检测到的特征点进行匹配
def matchKeypoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh):
# 建立暴力匹配器
matcher = cv2.BFMatcher()
# 使用KNN检测来自A、B图的SIFT特征匹配对,K=2
rawMatches = matcher.knnMatch(featuresA, featuresB, 2)
matches = []
for m in rawMatches:
# 当最近距离跟次近距离的比值小于ratio值时,保留此匹配对
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < m[1].distance * ratio:
# 存储两个点在featuresA, featuresB中的索引值
matches.append((m[0].trainIdx, m[0].queryIdx))
# 当筛选后的匹配对大于4时,计算视角变换矩阵
if len(matches) > 4:
# 获取匹配对的点坐标
ptsA = np.float32([kpsA[i] for (_, i) in matches])
ptsB = np.float32([kpsB[i] for (i, _) in matches])
# 计算视角变换矩阵
(H, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsA, ptsB, cv2.RANSAC, reprojThresh)
# 返回结果
return (matches, H, status)
# 如果匹配对小于4时,返回None
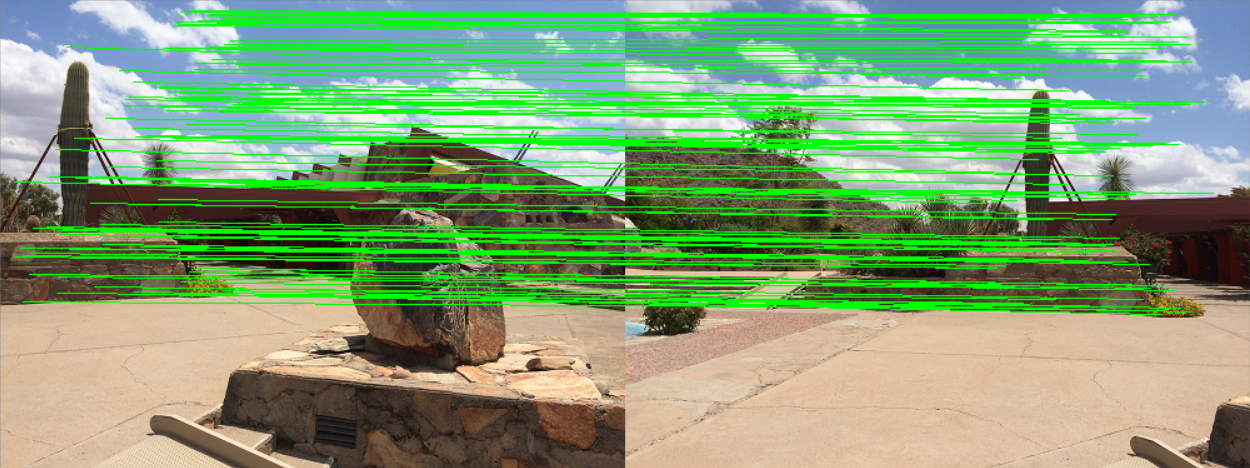
return None3. 将匹配的特征点可视化
def drawMatches(imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status):
# 初始化可视化图片,将A、B图左右连接到一起
(hA, wA) = imageA.shape[:2]
(hB, wB) = imageB.shape[:2]
vis = np.zeros((max(hA, hB), wA + wB, 3), dtype="uint8")
vis[0:hA, 0:wA] = imageA
vis[0:hB, wA:] = imageB
# 联合遍历,画出匹配对
for ((trainIdx, queryIdx), s) in zip(matches, status):
# 当点对匹配成功时,画到可视化图上
if s == 1:
# 画出匹配对
ptA = (int(kpsA[queryIdx][0]), int(kpsA[queryIdx][1]))
ptB = (int(kpsB[trainIdx][0]) + wA, int(kpsB[trainIdx][1]))
cv2.line(vis, ptA, ptB, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# 返回可视化结果
return vis4. 图像拼接
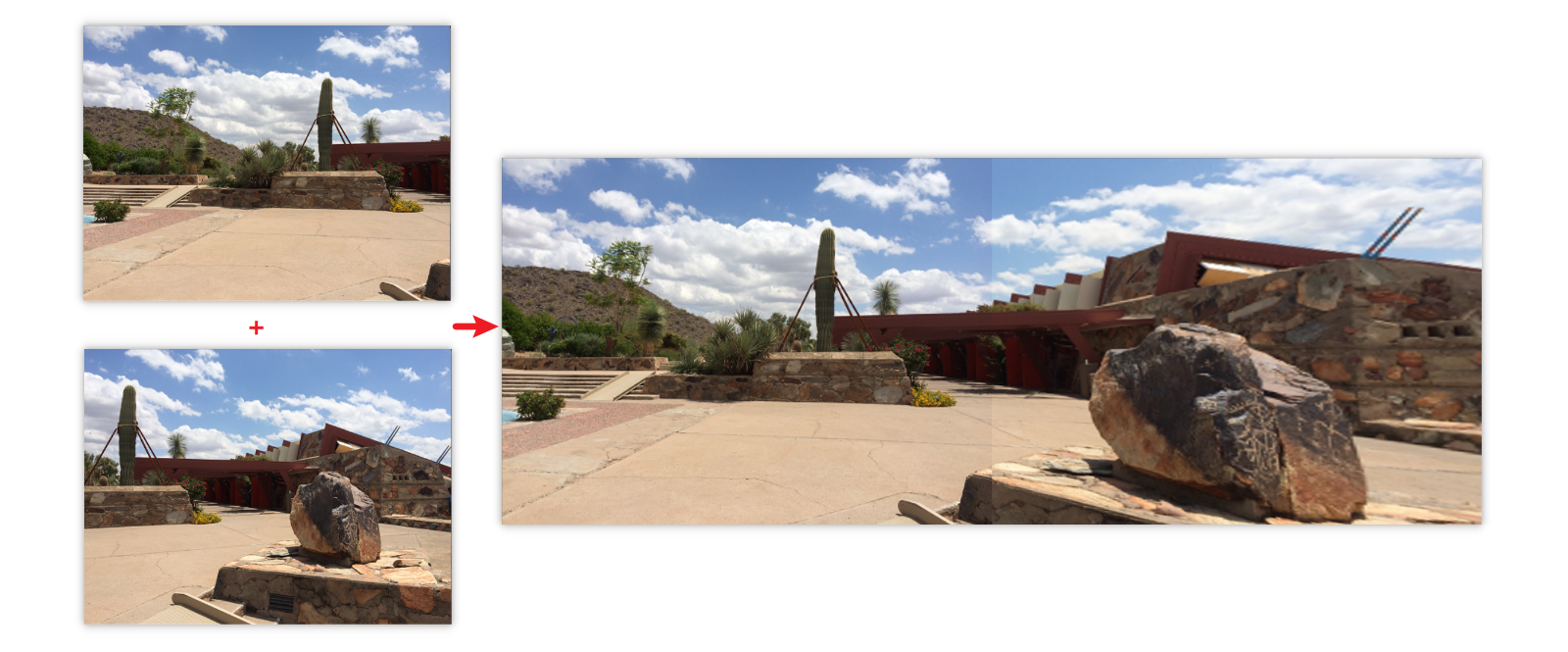
def stitch(images, ratio=0.75, reprojThresh=4.0,showMatches=False):
#获取输入图片
(imageB, imageA) = images
#检测A、B图片的SIFT关键特征点,并计算特征描述子
(kpsA, featuresA) = detectAndDescribe(imageA)
(kpsB, featuresB) = detectAndDescribe(imageB)
# 匹配两张图片的所有特征点,返回匹配结果
M = matchKeypoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh)
# 如果返回结果为空,没有匹配成功的特征点,退出算法
if M is None:
return None
# 否则,提取匹配结果
# H是3x3视角变换矩阵
(matches, H, status) = M
# 将图片A进行视角变换,result是变换后图片
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, (imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1], imageA.shape[0]))
cv_show('result', result)
# 将图片B传入result图片最左端
result[0:imageB.shape[0], 0:imageB.shape[1]] = imageB
cv_show('result', result)
# 检测是否需要显示图片匹配
if showMatches:
# 生成匹配图片
vis = drawMatches(imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status)
# 返回结果
return (result, vis)
# 返回匹配结果
return result